Installing Ansible Modules for A10 Networks
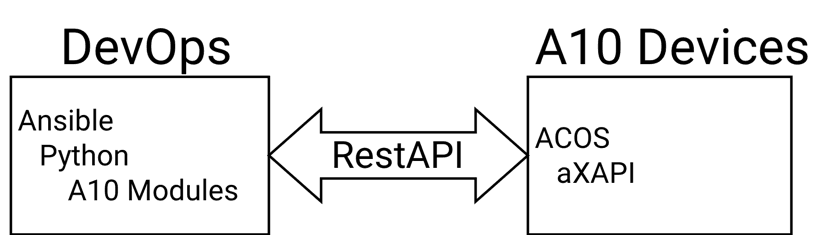
A10 Networks products are designed from the ground-up around an extensive set of Application Programming Interface (API) resources which can manage every aspect of each system. The A10 Networks API uses the RESTful API architecture to glue A10 Networks systems seamlessly to DevOps management systems and a wide variety of other technologies.
Ansible is an automation system for deploying and managing computer software and hardware environments. Ansible modules are software programs used by Ansible to perform specific tasks. The A10 Networks Ansible library of modules perform the function of translating the Ansible command to the specific A10 Networks API format and performs the RESTful interface to A10 Networks products and services.
This article will describe how to install the A10 Networks module libraries onto a Linux system with Ansible installed and operating.
Background
The A10 Networks Ansible module library contains a large number of programs written in Python. To enable DevOps systems to manage A10 Networks devices, the A10 Networks Ansible library needs to be installed onto the system running Ansible. Once the A10 Networks Ansible module library is installed, Ansible scripts are then able to interface with A10 Networks systems.
Download the A10 Networks Module Library
A10 Networks Ansible module libraries are located on GitHub here a10-ansible.
There are several versions of the A10 Networks modules located under different branches. The master branch is available to anyone. Other branches contain additional modules. To access the latest versions of the A10 Networks modules, you should contact your local A10 Networks sales representative to provide access and guidance.
Select the library version and click on the “Clone or Download” button to download the library. Move this library to the Ansible server.
Install the A10 Networks Module Library
The GitHub website for the A10 Networks Ansible modules describes the procedure to install this library using the standard and appropriate methods. Described is installations with PIP and PyPi.
This article will describe the installation of the A10 Networks modules manually. This will help administrators to customize installations to meet local IT standard practices.
Install overview steps:
- Go to the directory where the A10 Networks ansible library was downloaded. This can be any temporary or source folder.
- Unzip the library. This will unload several folders of code and scripts. The Ansible modules and additional Python software is all that will be required.
- Copy the A10 Networks Ansible modules folder to your specific ansible modules folder.
- Copy the A10 Networks Python modules to your Python site-packages folder.
The following is an example bash script.
#!/usr/bin/bash
#This example, the sdk_development version of the A10 Networks Modules library was downloaded
A10 NetworksANSIBLELIB=a10-ansible-sdk_development.zip
A10 NetworksDIR=${A10 NetworksANSIBLELIB::-4}
#This example, the python library is hard coded for simplicity. Your environment may likely vary
ANSIBLEMODS="/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible/modules"
PYTHONMODS="/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/"
#CD to the folder with the A10 Networks library zip file and unzip the contents
HERE=`pwd`
unzip -q $A10 NetworksANSIBLELIB
cd $HERE/$A10 NetworksDIR/a10_ansible
#The Ansible modules are stored in the "library" folder. We are renaming this folder and moving it to the Ansible modules library.
mv library/ $ANSIBLEMODS/a10_ansible_modules
#Also included are several Python common modules which need to be copied to the Python site-packages library like any other software package
mv $HERE/$A10 NetworksDIR/a10_ansible $PYTHONMODS
Be aware that your specific environment will vary depending on versions of Python, Linux and the A10 Networks Modules Library. The script commands can be run one at a time manually.
The A10 Networks Modules distribution also contains a folder named "examples" which contains Ansible playbook example YAML templates for each Ansible module.
Create the following file in the playbook folder as "ansible.cfg"
[defaults]
library = /usr/share/a10_ansible_modules/
module_utils = /usr/share/a10_ansible/
Change the folder paths as appropriate.
Testing A10 Networks Ansible Modules
The following Ansible configuration will initialize a single A10 Networks Thunder ethernet interface. The steps performed are:
- Log into the A10 Networks virtual or hardware system
- Enable the specified Ethernet Interface
- Configure the interface for DHCP
Create a folder and CD to this folder.
Create an Ansible hosts inventory file. This file will contain the address of one or more A10 Networks systems.
#/usr/bin/bash
echo "[all]" > ./hosts
echo 192.168.1.100 >> ./hosts
In this example, the A10 Networks systems Management IP address is 192.168.1.100.
Create a custom ansible.cfg file in the local folder.
[defaults]
host_key_checking = False
Since we are connecting with REST instead of SSH, we need to disable the requirement to check remote host keys. This parameter can also be added to the main Ansible configuration, usually at /etc/ansible.cfg.
Create an Ansible playbook YAML file. This will have two Ansible variables.
- inventory_hostname is an Ansible built-in variable passed from the hosts file
- ifnum is the Ethernet interface number and is passed from the command line during execution.
- connection: is required since REST is used instead of SSH to interface with the A10 Networks system.
- name: Update A10 Networks ACOS system Ethernet interface
connection: local
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Update Ethernet 1 Interface - IP Address, Enable
a10_interface_ethernet:
a10_host: "{{ inventory_hostname }}"
a10_username: "admin"
a10_password: "a10"
state: "present"
action: "enable"
ifnum: "{{ ifnum }}"
ip:
dhcp: "true"
Save this to a file named "init_ethernet_interface.yml".
Run the following command to execute the playbook which calls the A10 Networks module "a10_interface_ethernet".
ansible-playbook -i hosts init_ethernet_interface.yml --extra-vars "ifnum=1" -v
Another playbook example to initialize the Management interface.
- name: Update vThunder CFW for initial use - Network, DNS, etc.
connection: local
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Update Management Interface - IP Address, Enable
a10_interface_management:
a10_host: "{{inventory_hostname}}"
a10_username: "admin"
a10_password: "a10"
state: "present"
action: "enable"
ip:
dhcp: "true"
default-gateway: "172.20.0.1"
Troubleshooting
ANSIBLE_DEBUG=True
Seeing is believing.
Schedule a live demo today.